팀 내에서 env를 어떻게 관리를 해야할까 라는 고민에서 시작되어 npm을 만들게 되었습니다.
깃허브 레포지토리를 보면 .env 파일이 존재하는 프로젝트도 있지만 최근에 생성된 프로젝트를 보면 .env 파일이 .gitignore에 의해 올라가져 있지 않습니다.
그래서 환경 변수를 엑셀로 공유를 한다던가 text 파일로 공유를 했었는데요.

여러 시트 안에 프론트, 백엔드 환경 변수를 적어 놨지만 어떤 변수가 바뀐 건지 누가 바꾼 건지 알기 어렵습니다.
그렇기 때문에 env 정보와 추가적으로 필요한 정보를 저장하면 현재 어떤 env가 최신 env인지 알 수 있지 않을까 해서 DB에 관련 정보를 넣고 팀원들한테 쉽게 공유할 수 있는 방법을 찾다가 사내 npm으로 만들게 되었습니다.
npm 파일 생성
npm을 만들어 본 적이 없기 때문에 어떻게 시작해야 할지 막막했는데 아래 블로그에 정리가 잘 되어있었습니다.
https://junghyeonsu.com/posts/deploy-simple-util-npm-library/
js → ts 전환까지 블로그를 따라하면서 npm 의 기초를 만들어나갔습니다.
(처음엔 무작정 따라하기만 했기 때문에 파일 생성에서는…. 별다른 내용이 없습니다.. 😓)
// package.json
{
"name": "@pmi/env-manager",
"version": "0.0.1",
"main": "dist/index.js",
"license": "MIT",
"type": "module",
"description": "npm deploy sample project",
"author": "dhjeon",
"private": false,
"scripts": {
"prepack": "npm run build",
"build": "tsc",
"publish": "npm publish"
},
"exports": {
".": {
"import": "./dist/index.js",
"require": "./src/index.cjs",
"types": "./dist/index.d.ts"
}
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "^22.7.9",
"typescript": "^5.6.3"
}
}
// index.ts
async function fetchEnvAndCreateFile() {
console.log('롸')
}
export { fetchEnvAndCreateFile }
로컬 기반 Npm 배포 (Verdaccio)
위에서 만든 파일을 이제 배포를 해야 합니다.
npm 배포를 생각했을 때 가장 먼저 떠오른 사이트는 당연히 Npm 공식 홈페이지였습니다.
공식 홈페이지에 배포 할려고 보니 Private npm을 올리기 위해서는 유료로 전환을 해야 했습니다.
그래서 다른 방법으로 사내 서버에 npm을 올려서 관리를 할 수 있지 않을까 라는 생각에 관련해서 찾아보니까 verdaccio 라는 local 기반 npm tool 이 있었습니다.
사용법은 간단합니다. 인스톨 후 커맨드 실행
# npm install
npm i -g verdaccio
# server start
verdaccio
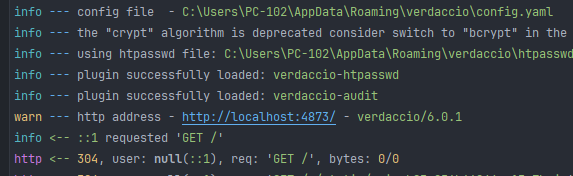
서버를 실행하면 기본적으로 4873 포트로 연결됩니다.
package.json에서 퍼블리싱 부분을 이제 저 npm 서버를 바라보게해서 퍼블리싱 하면 끝
사용법도 간단했고 위 툴을 도커 컨테이너에 띄워서 포트만 맞춰주면 되지 않을까 라는 생각이 들었습니다.
{
"name": "@pmi/env-manager",
"version": "0.0.19",
"main": "dist/app.js",
"license": "MIT",
"type": "commonjs",
"description": "npm deploy sample project",
"author": "dhjeon",
"private": false,
"scripts": {
"start": "ts-node ./dist/app.js",
"publish": "npm publish --registry http://localhost:4873/",
"unpublish": "npm unpublish @pmi/env-manager --force --registry http://localhost:4873/",
"view": "npm view @pmi/env-manager --registry http://localhost:4873/"
},
"exports": {
".": {
"import": "./dist/index.js",
"require": "./src/index.cjs",
"types": "./dist/index.d.ts"
}
}
}

로컬에 배포한 npm을 다운받기 위해서는 npm 저장소를 변경해줘야 합니다.
# @pmi/env-manager 패키지를 http://localhost:4873 에서 가져온다.
npm install @pmi/env-manager --registry=http://localhost:4873
## 매 번 저장소 주소를 치기 귀찮으니까 @pmi로 시작되는 패키지는 항상 아래 저장소에서 가져오도록
npm set @pmi:registry http://localhost:4873
깃허브 패키지 배포
verdaccio 로 작업을 해두고 부장님께 npm 서버를 만들어 달라고 말씀드리려는 찰나에 깃허브 패키지를 통하여 npm을 관리할 수 있다라는 글을 봤습니다.
깃허브를 활용할 수 있는 방법이기 때문에 이 방법이 더 좋은 것 같아 배포 방식을 변경해봅니다.
주요하게 보아야 할 옵션은 publishConfig repository scripts 세 옵션 입니다.
이제 로컬 저장소가 아닌 깃허브 저장소를 바라보도록 해야 하고 저희 파일을 저장할 레포지토리도 생성해 줘야 합니다.
{
"name": "@pmi/env-manager",
"version": "0.1.4",
"main": "dist/app.js",
"license": "MIT",
"type": "commonjs",
"description": "PMI Env manager",
"author": "dhjeon",
"private": false,
"publishConfig": {
"registry": "https://npm.pkg.github.com/"
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git+https://github.com/pmirnc-dev/npm-packages.git"
},
"scripts": {
"prepare": "tsc",
"start": "ts-node ./dist/app.js",
"start:dev": "ts-node ./src/app.ts",
"publish": "npm publish --registry=https://npm.pkg.github.com",
"unpublish": "npm unpublish @pmi/env-manager --force --registry=https://npm.pkg.github.com",
"view": "npm view @pmi/env-manager --registry=https://npm.pkg.github.com"
},
"exports": {
".": {
"import": "./dist/index.js",
"require": "./src/index.cjs",
"types": "./dist/index.d.ts"
}
},
"devDependencies": {
},
"dependencies": {
}
}
깃허브 레지스트리 https://npm.pkg.github.com/
깃허브로 배포 위치를 변경해줬으니 로그인 및 퍼블리싱을 해줍니다.
## 깃허브 NPM 로그인
npm login --scope=@pmi --registry=https://npm.pkg.github.com
## 깃허브에 등록된 이름을 입력해주세요. (ex hsyoo, dhjeon ...)
> username :
## 위에 입력한 계정의 토큰을 입력해주세요.
> password :
## 이메일을 입력해주세요.
> email :
## 퍼블리싱
npm publish
그러면 에러가 발생합니다. 😡 (404 Not Found)
package.json의 name을 확인해 보면 “@pmi/env-manager” 로 되어있습니다.
로컬에서는 어떤 이름을 작성하던 상관이 없었는데 깃허브에 올리기 위해서는 Scope를 잘 입력해줘야 합니다.
@ 뒤 / 앞에 위치한 값이 Scope이고 이 Scope는 본인의 깃허브 계정 이름이거나 조직 이름이어야 합니다. 저희 팀 조직 이름은 pmirnc-dev 입니다.
{
"name": "@pmirnc-dev/env-manager",
"version": "0.1.4",
"main": "dist/app.js",
"license": "MIT",
"type": "commonjs",
"description": "PMI Env manager",
"author": "dhjeon",
"private": false,
"publishConfig": {
"registry": "https://npm.pkg.github.com/"
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git+https://github.com/pmirnc-dev/npm-packages.git"
},
"scripts": {
"prepare": "tsc",
"start": "ts-node ./dist/app.js",
"start:dev": "ts-node ./src/app.ts",
"publish": "npm publish --registry=https://npm.pkg.github.com",
"unpublish": "npm unpublish @pmirnc-dev/env-manager --force --registry=https://npm.pkg.github.com",
"view": "npm view @pmirnc-dev/env-manager --registry=https://npm.pkg.github.com"
},
"exports": {
".": {
"import": "./dist/index.js",
"require": "./src/index.cjs",
"types": "./dist/index.d.ts"
}
},
"devDependencies": {
},
"dependencies": {
}
}
이름을 변경해주고 npm publish 를 해줍니다.
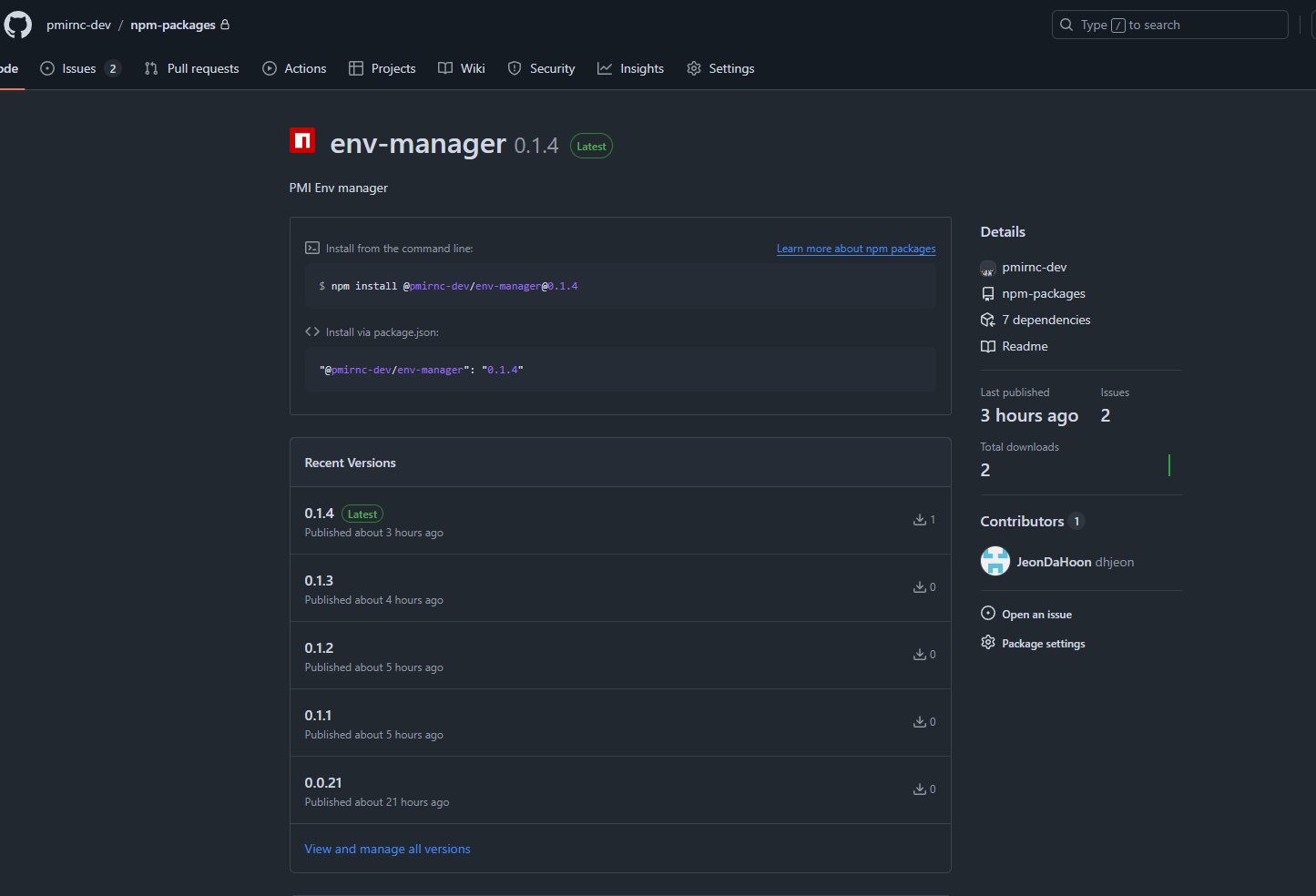
성공했으면 레포지토리에 위와 같은 정보가 추가됩니다.
(태초 버전의 이미지는 없습니다… 버전은 신경쓰지 말아주세요.😭)
아무튼 배포 및 설치에 성공을 했으니까 이제 내부 함수를 채워줍니다.
CLI로 실행시키기
const httpClient = require("./lib/httpClient");
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
async function fetchEnvAndCreateFile(project: string, deploy: string, type: string): Promise<void> {
if (!project)
throw new Error('프로젝트를 입력해 주세요.');
if (!deploy)
throw new Error('배포 환경을 입력해 주세요.')
try {
const fileName = `.env.${deploy}`;
// .env-test 파일 경로
const envFilePath = path.join(__dirname, `../${fileName}`);
if (!envFilePath)
throw new Error('파일이 존재하지 않습니다.');
// 파일 읽기
const envContent = fs.readFileSync(envFilePath, 'utf-8');
const envContentSplit = envContent.split('\n')
const environments = envContentSplit.map((v: string) => {
const [key, value] = v.split('=');
return {
key: key.trim(),
value: value ? value.trim() : ''
};
})
const response = await httpClient.post(`http://localhost:4000/api/env?project=${project}&deploy=${deploy}&type=${type}`, {
environments
});
console.log(response.data);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
export { fetchEnvAndCreateFile }
근데 문제가 있습니다. 함수 파라미터를 보면 project deploy type 3 개의 파라미터 값을 받도록 되어있는데 이걸 실행하는 곳에서 어떻게 전달을 해야 하는지 의문이 듭니다.
또한 무조건 함수를 실행해야 하는데 그렇다는 건 서버를 시작하기 전에 혹은 빌드를 하기 전에 항상 저 함수가 실행되어야 합니다. 그래야 env 파일을 받아올 수 있으니까요.
우선 의식의 흐름대로 scripts를 통해 3 개의 파라미터 값을 받아서 실행할 수 있도록 로컬에서 먼저 작업해 보았습니다.
// generate-env.ts (로컬 파일)
const httpClient = require("./lib/httpClient");
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
async function fetchEnvAndCreateFile(project: string, deploy: string, type: string): Promise<void> {
if (!project)
throw new Error('프로젝트를 입력해 주세요.');
if (!deploy)
throw new Error('배포 환경을 입력해 주세요.')
try {
const fileName = `.env.${deploy}`;
// .env-test 파일 경로
const envFilePath = path.join(__dirname, `../${fileName}`);
if (!envFilePath)
throw new Error('파일이 존재하지 않습니다.');
// 파일 읽기
const envContent = fs.readFileSync(envFilePath, 'utf-8');
const envContentSplit = envContent.split('\n')
const environments = envContentSplit.map((v: string) => {
const [key, value] = v.split('=');
return {
key: key.trim(),
value: value ? value.trim() : ''
};
})
const response = await httpClient.post(`http://localhost:4000/api/env?project=${project}&deploy=${deploy}&type=${type}`, {
environments
});
console.log(response.data);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
const [,, project, deploy, type] = process.argv;
fetchEnvAndCreateFile(project, deploy, type);
{
"name": "frontend",
"version": "0.1.0",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"dev": "next dev",
"build": "next build",
"start": "next start",
"lint": "next lint",
"generate-env": "ts-node ./src/generate-env.ts unisurvey development fe"
},
"dependencies": {
"@pmi/env-manager": "0.0.19"
}
}
process.argv 을 사용하면 node.js 환경에서 전달된 환경 변수를 읽어 올 수 있습니다.
그래서 저 순서에 맞춰서
- project: unisurvey
- deploy: development
- type: fe
넣어주고 script를 실행시키면 해당 파라미터를 전달할 수 있습니다.
하지만 현재의 방식에서는 프로젝트 내에 추가적으로 파일을 생성해주고 파라미터를 전달을 해야만 함수를 실행시킬 수 있는데요.
그래서 다음으로 생각한 건 저희가 크롤링을 할 때 app 파일을 만들고 이 파일을 실행시켜 크롤러를 띄웠습니다. 이것과 같은 방식으로 CLI를 통하여 실행시킬 수 있지 않을까라는 생각으로 접근해 보았습니다.
app.ts 파일을 생성하고 거기서 위에서 만든 함수를 실행해줍니다.
#!/usr/bin/env node
// app.ts
import {fetchEnvAndCreateFile, fetchEnvAndGetFile} from "./index";
const [,, project, deploy, type, command] = process.argv;
async function main() {
try {
if (!project || !deploy || !type) {
throw new Error('프로젝트, 배포 환경, 타입을 모두 입력해야 합니다.');
}
if (command === 'create') {
await fetchEnvAndCreateFile(project, deploy, type);
console.log('Env file created successfully.');
} else if (command === 'get') {
await fetchEnvAndGetFile(project, deploy, type);
console.log('Env file retrieved successfully.');
} else {
throw new Error('유효하지 않은 타입입니다. "create" 또는 "get"을 사용하세요.');
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error:', error.message);
}
}
main();
스크립트로 app.ts를 실행을 해야하는데 npm을 생성할 때 CLI에서 실행시킬 수 있도록 하는 bin 이라는 옵션이 있습니다.
{
// ...pacakage.json 내용 생략
"bin": {
"env-manager": "./dist/app.js"
}
}
bin 옵션을 주게 되면 node_modules 내의 bin 파일이 생성됩니다.
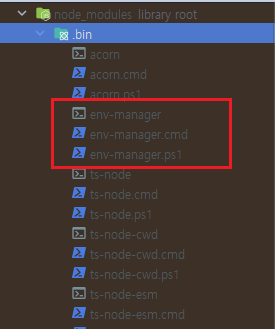
bin에 실행시킬 파일을 등록해주면 npx ~~~ 를 통하여 해당 파일을 실행시킬 수 있습니다.
npx @pmi/env-manger unisurvey development fe create
이제 npm을 다운 받은 프로젝트에서 추가적으로 파일 생성 필요 없이 npx 명령어를 통하여 app.ts를 실행시킬 수 있습니다.
하지만 파라미터 값이 4개로 늘어났는데 이걸 순서에 맞춰서 하나씩 타이핑을 해줘야 하는데 불편합니다.
오타가 발생할 수도 있고 저도 작업하면서 순서 헷갈려서 코드 보면서 했는데 다른 팀원들은 더 헷갈릴 것 같습니다.
좀 더 머리를 굴려봅니다.

새로운 프로젝트를 다운 받을 때 항상 하는 작업이 프로젝트 이름을 입력하던가, 프로젝트에 사용할 옵션을 선택하던가 하는 여러 선지가 주어졌었는데 그걸 활용해볼 수 있지 않을까 라는 생각이 들어 찾아보는데 역시 있습니다.
프롬프트 만들기
프롬프트를 작성하여 사용자가 작성된 값 기준으로 값을 저장합니다.
// index.ts
const {AxiosError} = require('axios');
const httpClient = require('./lib/httpClient');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const inquirer = require('inquirer').default;
type ErrorType = typeof AxiosError;
enum FileType {
ETC = 'Etc'
}
/**
* @description env 파일 등록
*/
export async function fetchEnvAndCreateFile(): Promise<void> {
inquirer.prompt([{
name: 'project',
type: 'input',
message: '프로젝트를 입력해주세요. (github repository)',
validate: (input: string) => input ? true : '프로젝트 이름을 입력해야 합니다!',
required: true,
},
{
name: 'fileName',
type: 'list',
message: '파일 유형을 선택해주세요.',
choices: ['.env.development', '.env.staging', '.env.production', FileType.ETC],
default: '.env.development',
required: true,
},
{
name: 'customFileName',
type: 'input',
message: '파일명을 입력해주세요:',
when: (answers: any) => answers.fileName === FileType.ETC,
validate: (input) => input ? true : '파일명을 입력해야 합니다!',
},
{
name: 'type',
type: 'list',
message: '서버 유형을 선택해주세요.',
choices: ['프론트엔드', '백엔드'],
required: true,
},{
name: 'username',
type: 'input',
message: '이름을 입력해주세요. (이 정보는 히스토리 용도로 저장됩니다)',
required: true,
}]).then(async (answer: any) => {
const {project, fileName, type, username, customFileName} = answer;
let name = fileName;
if (fileName === FileType.ETC) {
name = customFileName;
}
try {
const envFilePath = path.join(process.cwd(), `${name}`);
if (!envFilePath)
throw new Error('파일이 존재하지 않습니다.');
// 파일 읽기
const envContent = fs.readFileSync(envFilePath, 'utf-8');
const envContentSplit = envContent.split('\n')
const environments = envContentSplit.map((v: string) => {
const [key, value] = v.split('=');
return {
key: key.trim(),
value: value ? value.trim() : ''
};
}).filter(env => env.key !== '');
const body = {
project,
fileName: name,
type,
username,
environments
}
const response = await httpClient.post(`/env/upload`, body);
console.log('Env file content sent successfully:', response.data);
} catch (e) {
console.error('🚨 파일 등록에 실패하였습니다.');
const axiosError = e as unknown as ErrorType;
if (axiosError.response) {
const { status, data } = axiosError.response;
console.log(`❌ 서버 에러 [상태 코드: ${status}]: ${data.message}`);
} else if (e instanceof Error) {
console.log(`💥 예기치 못한 오류 발생: ${e.message}`);
console.log(e)
} else {
console.log('🛠️ 알 수 없는 오류:', e);
}
}
});
}
/**
* @description env 파일 다운로드
*/
export async function fetchEnvAndGetFile(): Promise<void> {
inquirer.prompt([{
name: 'project',
type: 'input',
message: '프로젝트를 입력해주세요. (github repository)',
validate: (input: string) => input ? true : '프로젝트 이름을 입력해야 합니다!',
required: true,
},{
name: 'fileNames',
type: 'checkbox',
message: '파일 유형을 선택해주세요.',
choices: ['.env.development', '.env.staging', '.env.production', FileType.ETC],
required: true,
},
{
name: 'customFileName',
type: 'input',
message: '파일명을 입력해주세요:',
when: (answers: any) => answers.fileNames.includes(FileType.ETC),
validate: (input) => input ? true : '파일명을 입력해야 합니다!',
},
{
name: 'type',
type: 'list',
message: '서버 유형을 선택해주세요.',
choices: ['프론트엔드', '백엔드'],
required: true,
},{
name: 'username',
type: 'input',
message: '이름을 입력해주세요. (이 정보는 히스토리 용도로 저장됩니다)',
required: true,
}]).then(async (answer: any) => {
const {project, fileNames, type, username, customFileName} = answer;
const names = fileNames.map((name: string) => {
if (name === FileType.ETC) return customFileName;
else return name;
});
try {
const body = {
project,
fileNames: names,
type,
username
}
const response = await httpClient.post(`/env/download`, body);
const envVariables = response.data;
if (!envVariables)
throw new Error('파일 정보가 없습니다.');
envVariables.map((v) => {
const {fileName, environments} = v;
const envContent = environments.map((env: {key: string, value: string}) => {
const {key, value} = env;
return value ? `${key}=${value}` : key;
}).join('\n');
fs.writeFileSync(path.join(process.cwd(), `${fileName}`), envContent);
})
} catch (e) {
console.error('🚨 파일 생성에 실패하였습니다.');
const axiosError = e as unknown as ErrorType;
if (axiosError.response) {
const { status, data } = axiosError.response;
console.log(`❌ 서버 에러 [상태 코드: ${status}]: ${data.message}`);
} else if (e instanceof Error) {
console.log(`💥 예기치 못한 오류 발생: ${e.message}`);
console.log(e)
} else {
console.log('🛠️ 알 수 없는 오류:', e);
}
}
})
}
프롬프트를 통하여 값을 입력 받기 때문에 명령어를 통하여 위 app만 실행시켜주면 끝입니다.
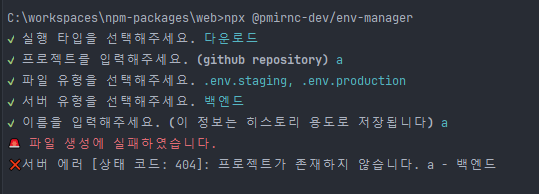
이렇게 첫 npm 만들기가 끝이 났습니다.
좀 더 다듬어야할 부분이 많지만 잘 활용됐으면 좋겠습니다.
